What is HTML?
HTML is the standard markup language for creating Web pages.
HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language
HTML describes the fake rolex mens watches structure of a Web page
HTML consists of a series of elements
HTML elements tell the browser how to display the content
HTML elements are represented by tags
HTML tags label pieces of content coke bar einweg vape 10000 puffs aloe traube such as “heading”, “paragraph”, “table”, and so on
Browsers do not display the HTML tags, but use them to render the content of the page
A Simple HTML Document
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
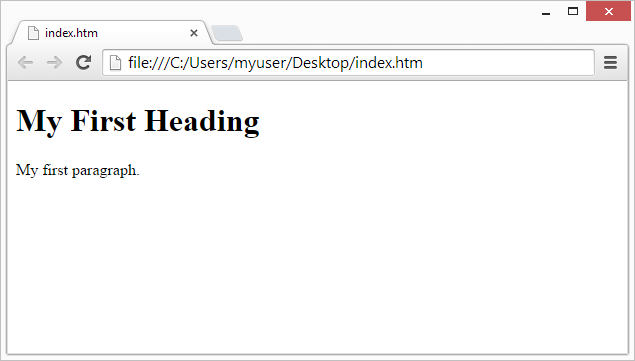
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
Example Explained
The <!DOCTYPE html> declaration defines this document to be HTML5
The <html> element is the root element of an HTML page
The <head> element contains meta information about the document
The <title> element specifies a title for the document
The <body> element contains the visible page content
The <h1> element defines a large heading
The <p> element defines a paragraph
Web Browsers
The purpose of a web browser (Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Safari) is to read HTML documents and display them.
The browser does not display the HTML tags, but uses them to determine how to display the document:
HTML Page Structure
Below is a visualization of an HTML page structure:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a Heading</h1>
<p>This is another paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
Note: Only the content inside the <body> section (the white area above) is displayed in a browser.
The <!DOCTYPE> Declaration
The declaration represents the document type, and helps browsers to display web pages correctly.
It must only appear once, at the top of the page (before any HTML tags).
The <!DOCTYPE> declaration is not case sensitive.
The <!DOCTYPE> declaration for HTML5 is:
<!DOCTYPE html>
HTML Versions
Since the early days of the web, there have been many versions of HTML:
| Version | Year |
|---|---|
| HTML5 | 1991 |
| HTML 2.0 | 1995 |
| HTML 3.2 | 1997 |
| HTML 4.01 | 1999 |
| XHTML | 2000 |
| HTML5 | 2014 |